What is the contraceptive ring?
- How does the contraceptive ring work?
- Contraceptive ring effectiveness
- Advantage of the contraceptive ring
- Side effects of the contraceptive ring
- Who can use the contraceptive ring?
- Can you use the contraceptive ring after giving birth?
- How to insert the NuvaRing
- How to check your contraceptive ring
- When can I start using NuvaRing?
- How to use the contraceptive ring
- Safe sex during your ring-free break
- Taking the contraceptive ring out
- What to do if the contraceptive ring comes out or you’ve used it incorrectly
- Other contraceptive options
The contraceptive ring (NuvaRing) is a plastic ring which can be placed into the vagina and used as a contraceptive. It’s a type of combined contraceptive, which means like the combined pill, it contains two hormones – oestrogen and progestogen.
Some women choose NuvaRing if they’re worried about forgetting a pill each day. NuvaRing is taken out after three weeks and lots of women choose to have a four or seven-day break from the ring before inserting the new one. In your break, you’ll likely have a withdrawal bleed. A withdrawal bleed is like a period, but it isn’t one, and it happens when you break from your ring.
How does the contraceptive ring work?
The contraceptive ring releases a continuous dose of hormones into the bloodstream through the vaginal wall. These hormones stop your ovaries from releasing an egg each month. But they also work to:
- Thicken the mucus from your cervix, making it difficult for sperm to travel through and reach an egg
- Thin the lining of the womb, making it harder for a fertilised egg to implant
Contraceptive ring effectiveness
NuvaRing is 99% effective when used correctly all the time. If it’s not always used correctly, 9 out of 100 users of the contraceptive ring will get pregnant.
Advantage of the contraceptive ring
The vaginal ring is a fairly popular contraceptive choice amongst women. This is most likely because you don’t have to think about it every day – you only change it every three weeks.
Other advantages of the ring include:
- It’s not affected if you’re sick or have diarrhoea
- You can choose whether to have a withdrawal bleed or not
- If you choose to take a break and have a withdrawal bleed, these can be more regular, less painful and lighter
- It can help with premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- It’s easy to insert and remove
- It can help with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- It can help with menopausal symptoms
- It can help reduce the risk of recurrent endometriosis after you’ve had surgery
Side effects of the contraceptive ring
Like with most contraceptives, there is a chance you’ll experience some side effects when using NuvaRing.
Potential temporary side effects
- Headaches
- Feeling nauseous
- Sore breasts
- Mood changes
- Vaginal discharge
Some people women also might experience spotting or unexpected bleeding for the first few months.
Risks
Like with most combined contraceptives, using the contraceptive ring does put you at higher risk of developing a blood clot. But there is evidence to suggest the risk is slightly higher with the ring than the combined pill. It’s also higher if:
- You smoke
- You’re overweight
- You’re not mobile for long periods of time or you’re a wheelchair user
- Someone in your immediate family has had a blood clot
There is also a small increased risk of breast or cervical cancer, but these reduce with time after stopping the ring.
Who can use the contraceptive ring?
The vaginal ring is suitable for lots of women.
Given the risks already mentioned there’s quite a few people who it’s not suitable for.
You might not be able to take the ring if:
- You’re 35 or over and smoke/have stopped smoking in the last year
- You’re overweight
- You’re taking certain medications, e.g. some treatments for epilepsy and HIV
- You’re breastfeeding a baby less than six weeks old
- You get migraines with aura
- You or your family have a history of blood clots
- You have certain conditions, e.g. high blood pressure, heart disease, lupus, diabetes with complications
Your clinician will be there to advise on what’s suitable for you. And they’ll check your blood pressure and BMI before they can prescribe it.
Can you use the contraceptive ring after giving birth?
You can use the ring from 21 days after giving birth, provided it’s comfortable and you’re not breastfeeding. If you’re breastfeeding it’s advised you don’t start the ring again until six weeks after birth, this is because it might affect your milk production.
If your start on the ring any later than 21 days after giving birth you should use condoms or avoid having sex for the first seven days.
After miscarriage
If you’ve sadly had a miscarriage and would like to go back on the ring, you can start it straight away and you’ll be protected straight away.
After an abortion
If you’ve had an abortion, you can start the ring straight away after and you’ll be protected.
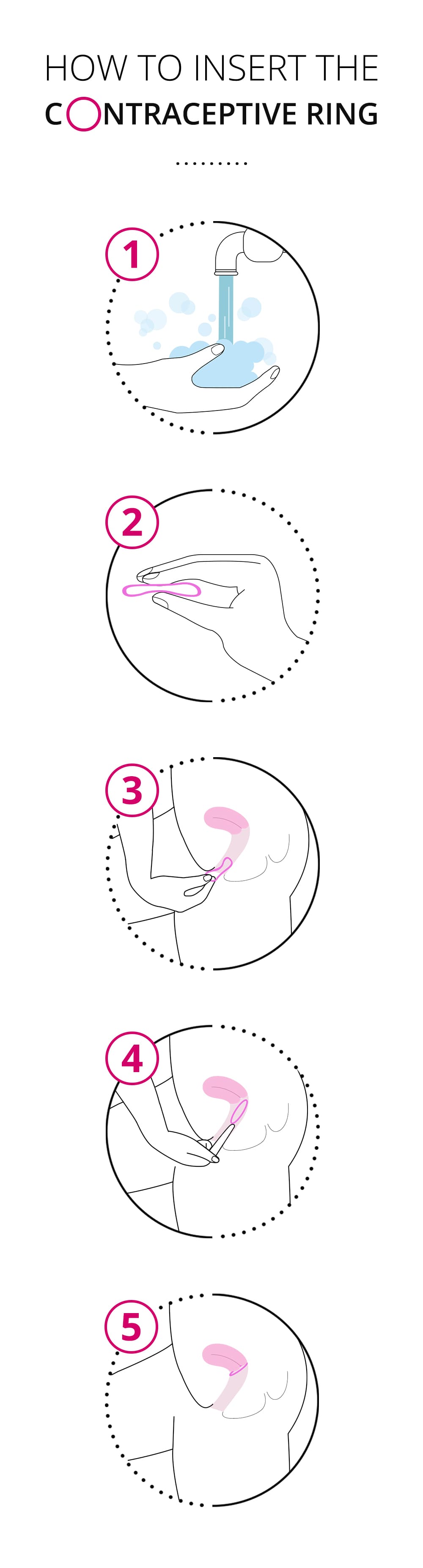
How to insert the NuvaRing
The vaginal ring should be inserted with clean hands.
- Squeeze the ring between your finger and thumb
- Push the ring into your vagina until it feels comfortable.
A clinician can advise you on how to put it in and take it out.
How long does it take to adjust to the ring?
Once the ring is inserted, most people won’t be able to feel it and you shouldn’t need any time to adjust to it.
What if my NuvaRing feels uncomfortable?
If the vaginal ring feels uncomfortable you can try pushing it a bit further into your vagina.
How to check your contraceptive ring
If you have the ring, you might be worried about checking it’s still there. There’s very little chance the ring will get lost because the cervix prevents it from going any further into your body. But if you’re sure you have it in and can’t feel it with your fingers it’s a good idea to see a clinician.
Does the ring hurt?
The ring shouldn’t hurt when you put it in or when it’s inside you. If you’re finding it painful, speak to a clinician.
Should I be able to feel my NuvaRing?
You shouldn’t be able to feel the ring as you go about your day, it shouldn’t bother you. But you should be able to feel it with your fingers inside your vagina.
Can my partner feel my NuvaRing?
Sometimes your partner might feel the ring during sex, but this wont be uncomfortable.
When can I start using NuvaRing?
If you’re sure you’re not pregnant you can start using the vaginal ring at any point in your cycle. You’ll be protected from pregnancy:
- Immediately – if you start on the first day of your period
- Immediately – if you start anytime between the first and fifth day of your period (provided you don’t have a very short or irregular menstrual cycle)
- After seven days – if you start the ring at any other time in your cycle. You’ll need to use other contraception, such as condoms, if you have sex during the first 7 days
How to use the contraceptive ring
NuvaRing was designed to be used for three weeks (21 days) straight, followed by a four or seven-day break.
How long can the ring stay in?
NuvaRing was designed to be used for three weeks (21 days) straight, followed by a four or seven-day break. In this break you’ll have a withdrawal bleed. This is like a period but isn’t one. It’s just your body’s reaction to the break in hormones. After this break you insert a new vaginal ring and start the cycle again.
Do you get a period on the NuvaRing?
In the four or seven-day break you’ll have a withdrawal bleed. This is like a period but isn’t one. It’s just your body’s reaction to the break in hormones. After this break you insert a new vaginal ring and start the cycle again.
If you want to skip your ‘period’
If you’d like to avoid the withdrawal bleed, or reduce the number of bleeds you have, there are different ways you can use Nuvaring:
- You can change your vaginal ring every three weeks for nine weeks in a row and then have a break for four or seven days. This is called tricycling. You’ll usually have a withdrawal bleed in your break. You then insert a new ring on the fifth or eighth day and start the cycle again.
- You can insert a new ring every three weeks with no break. This is called continuous use. You won’t have a withdrawal bleed, but you might get some bleeding. This should reduce as you use the vaginal ring over a long period of time.
- You can insert a new ring every three weeks for at least three weeks. If after this time you get bleeding that’s unacceptable to you for three to four days, you can take a four-day break and then insert a new ring. Use this ring for at least three weeks before changing it. This is called flexible extended use.
Safe sex during your ring-free break
You’re protected from pregnancy during your ring-free break provided:
- You used the vaginal ring correctly during the last three weeks
- You start the next ring cycle on time
- You’re not taking any treatments that will affect the vaginal ring. Medicines that may affect the ring include St John’s Wort and those used to treat epilepsy, HIV and TB. Check with your clinician about using the ring if you’re on any of these treatments.
Taking the contraceptive ring out
Using clean hands, you can use your fingers to take the ring out. The ring can’t get lost inside you as it’s stopped by the cervix. But if you’re having any problems taking it out, or can’t feel it, you can speak to a clinician and they will be able to advise you.
What to do if the contraceptive ring comes out or you’ve used it incorrectly
Like all contraception, you should try and use it correctly at all times. But occasionally you might forget to change your vaginal ring or put a new one in. It’s important you know what to do in these situations.
If the ring is removed outside the ring-free break
If it’s been less than 48 hours since the ring came out, you need to:
- Insert the ring as soon as possible
- Keep it in until the day you were supposed to take it out
You don’t need to use any extra contraception if:
- You’re in the first week after the ring-free break and you used the ring correctly in the week leading up to the break
- You’re in any other week of your cycle and you used the ring correctly in the seven days prior to it coming out
If it’s been more than 48 hours since the ring came out, you need to:
- Insert the ring as soon as possible
- Keep it in until the day you were supposed to take it out
- If you’re due to start a ring-free break in the next 7 days, don’t take it
- Use condoms or avoid sex until you’ve had a ring in place for seven days in a row
If you’re in the first week after a ring-free break and had unprotected sex in this week or the ring-free break you might need emergency contraception. You may also want to take a pregnancy test in three weeks’ time.
If you’re in any other week of your ring cycle you don’t need emergency contraception, provided you use the vaginal ring correctly in the previous seven days.
Ring has been left in longer than three weeks
If you’ve left the ring in for 28 days or less, you need to:
- Take your ring free break if you have one, insert a new ring after this and start the cycle as normal
- Insert a new ring straight away if you don’t take a break
You won’t need to use extra contraception, provided the ring was in place throughout the fourth week of use (days 21-28).
If you’ve left the ring in for more than four weeks and up to five weeks, you need to:
- Insert a new ring as soon as possible
- If you’re due to start a ring-free break, don’t take it.
- Use condoms if you have sex until the new ring has been in place for seven days
You don’t need emergency contraception as long as the ring was continuously in place for the last seven days.
If you’ve left the ring in for more than five weeks, you need to:
- Insert a new ring as soon as possible, don’t take a break even if you usually have one
- Use condoms if you have sex until the new ring has been in place for seven days
If you had unprotected sex in week five or later you might need emergency contraception. You might also need to take a pregnancy test in three weeks.
If you inserted the vaginal ring late after the break
If it’s less than eight full days since you removed your last ring:
- Insert a new ring now.
- Continue using the ring as normal.
If it’s eight or more full days since you removed your last ring:
Insert a new ring now.
- Keep this ring in until the day you usually change it.
- Use condoms or avoid sex for the next seven days.
If you had unprotected sex in the ring-free break you might need emergency contraception. You may also want to take a pregnancy test in three weeks’ time. Talk to a doctor, nurse or pharmacist as soon as possible.
Other contraceptive options
There are lots of other contraceptive options available.
Hormonal
Hormonal contraceptive options contain synthetic versions of hormones which work to protect you from pregnancy. Examples include:
- Combined pill
- Progestogen-only pill
- The patch
- The injection
- The implant
- Intrauterine system (IUS or hormonal coil)
Non-Hormonal
Non-hormonal contraceptive methods don’t use hormones, but things like barriers to protect you against pregnancy. These include:
- External condoms (male condoms)
- Internal condoms (female condoms)
- Diaphragm
- Cap
- Intrauterine device (IUD or non-hormonal coil)
- Fertility awareness methods (FAMs)
You can find out more by visiting our contraception advice hub here.
References



