What is trichomoniasis?
Reviewed by Dr Bhavini Shah
Trichomoniasis is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Google data shows that trichomoniasis gets 33,000 online searches on average per month in the UK alone. The World Health Organisation reported that there were 156 million new cases recorded globally in 2020. Luckily, trichomoniasis is also one of the most easily curable STIs.
Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasitic protozoan called Trichomonas vaginalis. Sometimes the STI is referred to as “trich” or trichomonas and you may see this name on online listings for STI tests or packaging.
We surveyed 500 British adults and found that, despite having so many Google searches, less than a third of people (29%) had heard of trichomoniasis before. It is now more important than ever to look out for signs that you or your partner may be infected.
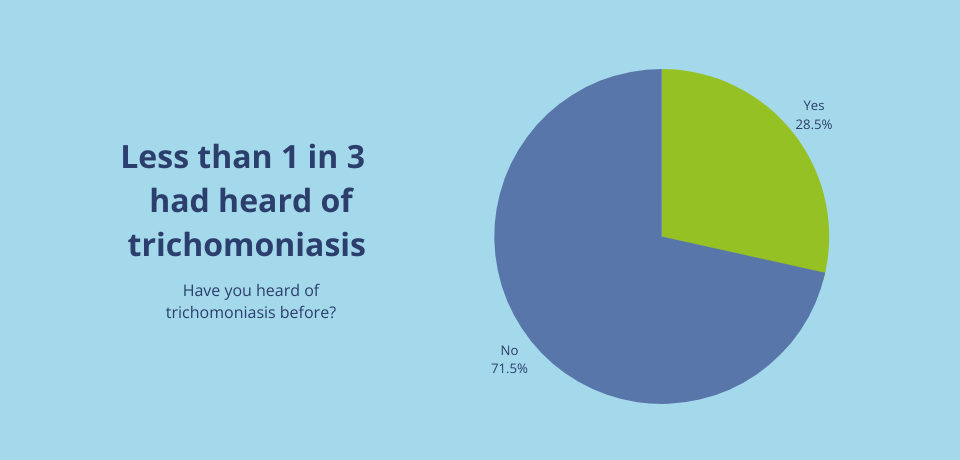
The STI can affect both men and women, although it doesn’t always show symptoms. In this article we’ll discuss the potential symptoms of trichomoniasis, complications of the STI and treatment available.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis
Symptoms of trichomoniasis can vary from person to person. Similarly to other STIs, some people might not experience any symptoms at all. In fact over half of people with the infection won’t have noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they differ slightly depending on your biological sex.
Shockingly, 80% of people said they would not feel confident in identifying the symptoms of trichomoniasis. Only 4% reported that they would be very confident in identifying the symptoms.

Trichomoniasis in men
Trichomoniasis in men can cause:
- Pain when peeing
- Needing to pee more than usual
- Pain during ejaculation (when you orgasm)
- Thin, white discharge from the penis
- Head of the penis may be red or swollen
- Penis is itchy or sore
Trichomoniasis in women
Trichomoniasis in women can cause vaginal problems, such as:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge which might be thick, thin, frothy or yellowy green
- Vaginal discharge may have an unpleasant smell
- More vaginal discharge than normal
- Vaginal itching, burning, or irritation
- Pain when peeing
- Pain during sex
If you have any of these symptoms, you should get tested for STIs as soon as possible. You can do this by visiting your GP, a sexual health clinic or a GUM clinic.
Trichomoniasis causes
Trichomoniasis, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. The trichomonas parasite affects the penis and vagina including the urinary tracts (where urine leaves the body).
Trichomoniasis is typically spread through sex without a condom. It’s spread from penis to vagina, vagina to penis and vagina to vagina. It’s not thought to be passed on during oral or anal sex, however you can catch it by sharing sex toys if they’re not cleaned between uses.
The best way to lower your chance of getting trichomoniasis is to use condoms and to get regular STI tests. You can get these for free from your GP, local GUM clinic or sexual health clinic. STI tests are also available to do at home from services such as Online Doctor, provided you don't have any symptoms.
Trichomoniasis complications
If left untreated, trichomoniasis can lead to health complications, although these are rare.
Trichomoniasis and HIV
Having trichomoniasis might increase the risk of contracting or transmitting other sexually transmitted infections, including HIV. To prevent catching or spreading other STIs you should use condoms when having sex.
Trichomoniasis and pregnancy
If you catch trichomoniasis while you’re pregnant and don’t get treatment the risk of you having your baby early increases. Your baby could also be born at a low birth weight. If you think you’ve been exposed to trichomoniasis you should speak to your GP or midwife.
Trichomoniasis test
Trichomoniasis symptoms are similar to other STIs which can make it difficult to diagnose. If you think you have trichomoniasis symptoms you should visit a GP or your local sexual health clinic clinic.
If you don’t have symptoms but think you have been exposed to the infection you can also use an at-home testing service like Online Doctor. We have STI tests for women and men, as well as tests for men who have sex with men, which you can discreetly complete at home.
If you have a positive result you should let your current sexual partner or partners and any other recent partners know. They should also get an STI test and treatment if necessary.
In our survey of 500 British adults, we found that the average person believes sexually active people should get themselves tested every time you (or your partner) has unprotected sex with another person. The next most common answers being every three months and every six months.
Getting tested regularly is best practice if you’re sexually active especially if you’re not using protection. We recommend being tested once every three months at a minimum if you are having frequent unprotected sex.
Trichomoniasis treatment
Trichomoniasis is usually quick and easy to treat. The infection is unlikely to go away on its own and can be easily passed to other sexual partners. If you have the infection, you’ll most likely be prescribed an antibiotic called metronidazole. These antibiotics work by killing the Trichomonas parasite. You'll usually have to take metronidazole twice a day, for up to a week. If the infection is more severe you may need to take the antibiotic for longer.
Your sexual partner or partners should also receive treatment, even if they don't have symptoms, to prevent reinfection. You should also avoid sexual activity until both you and your partner(s) have completed treatment and any symptoms have gone.
Once you’ve completed the treatment following your healthcare professional’s instructions, the infection should be gone. You may want to get retested to make sure the infection has been cleared completely.
Even though you’ve had treatment and the infection has gone you can still get the STI again. The best way to prevent this is by using condoms and getting regular STI tests.
References
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/trichomoniasis/
https://www.gov.uk/research-for-development-outputs/global-epidemiology-and-control-of-i-trichomonas-vaginalis-i
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trichomoniasis
Methodology
We conducted a OnePulse speed survey of 502 British over-18s on 30/10/2023 to understand what their knowledge was around trichomoniasis and attitudes towards STI testing. Google search data was gathered from Google Keyword Planner.





